Product in Mathematics Operations Factors Slope and Functions
Mathematics is built on precise definitions that explain how numbers, symbols, and expressions work together. Students often find it difficult to solve problems accurately, even when calculations seem simple. Concepts such as the order of operations, slope, product, factors, and functions form the core of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and higher-level mathematics.
We explain the most important and frequently searched math definitions, including what is the definition of order of operations in math, what is the definition of slope in math, what is the definition of product in math, and what is a factor in math definition. Each topic is explained with clear definitions, examples, and real-world applications to support strong conceptual understanding.
What Is the Definition of Order of Operations in Math
The order of operations is a set of rules used to determine the correct sequence for solving mathematical expressions that contain more than one operation.
Explanation
When an expression includes addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponents, or parentheses, the order of operations ensures that everyone arrives at the same correct answer. Without these rules, people might interpret mathematical expressions in multiple ways, which leads to incorrect results.
People commonly remember the order of operations using the acronym PEMDAS (also written as PEDMAS).
- P – Parentheses
- E – Exponents
- M – Multiplication
- D – Division
- A – Addition
- S – Subtraction
Multiplication and division are performed from left to right, as are addition and subtraction.
Example
- 2 + 5 × 3 = 17
- Multiplication is done first: 5 × 3 = 15
- Then addition: 2 + 15 = 17
Why It Matters
Understanding the order of operations also helps prevent common calculation errors and ensures consistency in mathematical problem-solving. Mastery of this concept builds a strong foundation for tackling complex expressions and real-world quantitative challenges.
What Is the Definition of Period in Math?
In mathematics, a period refers to the length of one complete cycle of a repeating pattern or function. It indicates how often a function repeats itself over a given interval. Understanding periods is crucial for analysing waves, oscillations, and cyclical phenomena in physics, engineering, and signal processing.
Explanation
People most commonly use the concept of period with trigonometric and periodic functions, such as sine and cosine. It tells us how often a function repeats over a specific interval. Understanding periods also helps in predicting patterns and modelling natural phenomena, from tides to seasonal changes.
Example
The sine function repeats every 2π, which is known as its period.
Applications
Periods are used in physics, astronomy, signal processing, sound waves, and any situation involving cycles or repetitive motion They are also essential in engineering and electronics for designing circuits and analysing repetitive signals.
What Is the Definition of Slope in Math?
Slope measures how steep a line is and indicates its direction on a graph. It is fundamental for understanding how one quantity changes relative to another, making it essential in predicting trends and making informed decisions. Slope also helps in comparing rates of change between different lines or functions.
Explanation
Slope measures how steep a line is and indicates its direction on a graph. It is fundamental for understanding how one quantity changes relative to another, making it essential in predicting trends and making informed decisions. Slope also helps in comparing rates of change between different lines or functions.
Slope Formula
- m=y2−y1x2−x1m = \frac{y_2 – y_1}{x_2 – x_1}m=x2−x1y2−y1
- m=x2−x1y2−y1
Example
- If a line passes through points (2, 3) and (6, 7):
- m=7−36−2=44=1m = \frac{7 – 3}{6 – 2} = \frac{4}{4} = 1m=6−27−3=44=1
- This indicates the line rises one unit vertically for every unit it moves horizontally.
Applications
Slope is a key concept in linear equations, motion graphs in physics, economic trends, and data analysis. It is also used in construction to determine gradients, in engineering to design ramps or roads, and in computer graphics to calculate angles and trajectories.
What Is the Math Definition of the Distributive Property
The distributive property allows multiplication to be applied across addition or subtraction within parentheses. It helps break down complex expressions into simpler parts, making calculations more manageable. This property also forms the foundation for advanced algebraic techniques like factoring and expanding polynomials.
Definition
a(b+c)=ab+ac
This shows how a single term outside the parentheses multiplies each term inside, ensuring accurate simplification and consistent results in calculations.
Example
3(4+5)=3×4+3×5=12+15=27
Using the distributive property prevents mistakes that might occur if parentheses are ignored and allows for quick mental math in daily problem-solving.
Importance
This property is essential for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding algebraic structure. It also supports problem-solving in real-life situations such as calculating totals, budgeting, or splitting quantities evenly. Mastery of the distributive property is crucial for progressing in algebra, geometry, and higher-level mathematics.
What Is a Factor in Math? (Factor Definition)
A factor is a number that divides another number exactly, without leaving a remainder.
Example
Factors of 12 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Applications
Factors are used in fraction simplification, prime factorisation, algebraic expressions, and number theory.
What Is the Definition of an Exponent in Math?
An exponent indicates how many times a base number is multiplied by itself.
Example
23=2×2×2=82^3 = 2 × 2 × 2 = 823=2×2×2=8
Applications
Exponents are used in scientific notation, population growth models, compound interest, computer algorithms, and physics formulas.
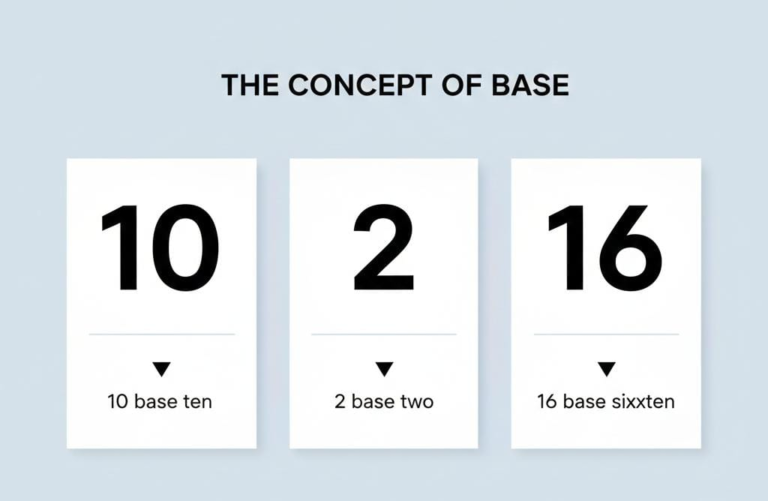
What Is the Definition of a Base in Math?
The base is the number that is repeatedly multiplied when an exponent is applied.
Example
In 525^252, 5 is the base and 2 is the exponent.
Importance
Bases appear in exponential expressions, logarithms, number systems, and advanced mathematical functions.
What Is the Definition of a Function in Math?
A function is a relationship where each input corresponds to exactly one output.
Example
- f(x)=2x+3f(x) = 2x + 3f(x)=2x+3
- If x = 4, then f(4) = 11.
Applications
Functions are used to model real-world relationships in physics, economics, engineering, computer science, and data science.
What Is the Definition of a Solution in Math?
A solution is a value that satisfies a mathematical equation or inequality.
Example
- 2x+5=112x + 5 = 112x+5=11
- x = 3 is the solution.
Why It Matters
Solutions are central to algebra, optimisation problems, and scientific modelling.
What Is the Definition of Product in Math?
The product results when you multiply two or more numbers, variables, or expressions together.
Simple Definition
Product = Result of multiplication
Basic Examples
- 4 × 5 = 20 Product is 20
- 6 × 3 = 18 Product is 18
- 2 × x = 2x Product is 2x
Product in Algebra
In algebra, products often involve variables and expressions.
Examples
- 3 × x = 3x
- 2a × 5b = 10ab
- (x + 2)(x + 3) = x² + 5x + 6
These results are all products formed by multiplication.
Factors and Product Relationship
The values being multiplied are called factors, and the final answer is the product.
Example
- 7 × 8 = 56
- Factors: 7 and 8
- Product: 56
This relationship is essential for understanding factorisation and divisibility.
Product of More Than Two Numbers
A product can involve multiple values.
Example
2 × 3 × 4 = 24The product of three numbers is 24.
Product in Geometry
Products are used to calculate measurements such as area and volume.
Examples
- Area of a rectangle = Length × Width
- Volume of a box = Length × Width × Height
- 8 × 5 = 40 square units (area)
Product in Real Life
Products appear in many everyday situations, including:
- Total cost = price × quantity
- Distance = speed × time
- Salary = hours worked × hourly rate
- Total items = number of groups × items per group
Product vs Sum (Common Confusion)
Many learners confuse product with sum.
- Sum Result of addition
- Product Result of multiplication
Example
- 4 + 6 = 10 (sum)
- 4 × 6 = 24 (product)
Why Understanding Product Is Important
Understanding the product helps students:
- Master multiplication and division
- Simplify algebraic expressions
- Solve equations accurately
- Apply formulas in science and finance
- Prepare for advanced math topics
The concept of product is foundational for polynomials, matrices, calculus, and statistics.
Conclusion
Understanding essential math definitions such as the order of operations, slope, product, factors, exponents, functions, and solutions creates a strong foundation for mathematical success. These concepts connect and appear across arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and real-world problem-solving.
By mastering mathematical vocabulary, students develop confidence, accuracy, and logical reasoning skills.
These definitions remain indispensable tools. Mastery of these concepts enhances problem-solving efficiency and supports higher-level mathematical thinking. A strong grasp of these fundamentals ensures long-term success in academic and real-world applications.
Learning Tips
- Order of Operations Always follow PEMDAS Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication/Division, Addition/Subtraction. Use practice exercises to strengthen accuracy.
- Period Identify repeating patterns in functions or waves; visual graphs help understand cycle lengths.
- Slope Remember slope = rise/run. Draw lines on grids and calculate changes in y over x for better understanding.
- Distributive Property Break expressions into smaller parts using a(b + c) = ab + ac. Practice expanding brackets regularly.
- Factors List all numbers that divide a given number exactly. Factor trees help in prime factorisation.
- Exponent Memorize powers of common bases (2, 3, 5, 10). Understand that exponents are repeated multiplication.
- Base In powers, the base is multiplied repeatedly. Visualizing exponents as repeated groups helps comprehension.
- Product Always multiply the numbers or terms; distinguish clearly from addition (sum). Practice with both numbers and variables.
FAQs
What is the definition of order of operations in math?
It is a set of rules (PEMDAS) that determines the sequence for solving expressions with multiple operations.
What is the definition of slope in math?
Slope measures how steep a line is and calculates the ratio of vertical change to horizontal change (rise/run).
What is the math definition of the distributive property?
It applies multiplication across addition or subtraction: a(b + c) = ab + ac.
What is a factor in math definition?
A factor divides another number exactly, without leaving a remainder.
What is the definition of an exponent in math?
A factor divides another number exactly, without leaving a remainder.
What is the definition of a base in math?
The base is the number you multiply repeatedly when applying an exponent.
What is the definition of product in Mathematics?
A product results when you multiply two or more numbers or expressions together.