Definition of Inequality in Math Slope Exponent Factor and More
Mathematics is a universal language, and understanding its fundamental terms is essential for success in academics and practical applications. From algebra and geometry to calculus and statistics, key mathematical concepts serve as the building blocks of problem-solving. This article explains some of the most important math definitions, including inequality, order of operations, period, slope, distributive property, factor, and exponent, offering clear examples and practical explanations.
Mathematics shapes how we analyse problems, make decisions, and understand patterns in the world around us. Mastering these foundational concepts not only improves academic performance but also strengthens critical thinking and logical reasoning skills. Whether for school, work, or everyday life, a solid grasp of these terms provides a reliable toolkit for solving complex problems efficiently.
What is the Definition of Inequality in Math?
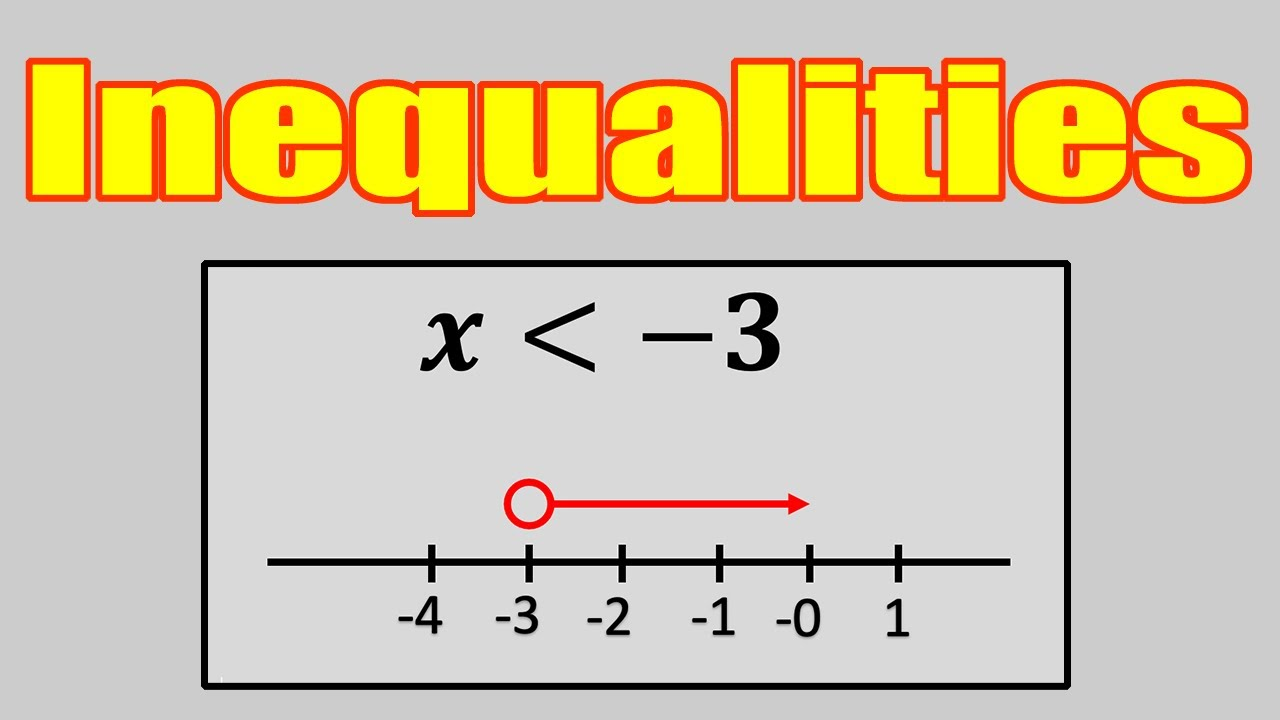
In mathematics, an inequality represents a relationship between two values or expressions that are not necessarily equal. Unlike equations, which state that two quantities are exactly the same, inequalities indicate that one value is greater than, less than, greater than or equal to, or less than or equal to another value.
The common symbols used in inequalities include
- > : greater than
- < : less than
- ≥ : greater than or equal to
- ≤ : less than or equal to
Example
If x>5x > 5x>5, this means that xxx can be any number greater than 5. Inequalities are widely used in algebra, economics, and real-life situations such as budgeting and comparing quantities.
What is the Definition of Order of Operations in Math
The order of operations refers to a set of guidelines that determine the proper sequence for solving mathematical expressions. Following these rules ensures calculations are performed correctly and consistently. A common way to remember the sequence is with the acronym PEMDAS.
- P: Parentheses first
- E: Exponents (powers and roots)
- M: Multiplication
- D: Division (from left to right)
- A: Addition
- S: Subtraction
Example
For the expression 2+3×(42−5)2 + 3 \times (4^2 – 5)2+3×(42−5), you first solve inside the parentheses, then calculate the exponent, followed by multiplication and addition:
- 42=164^2 = 1642=16
- 16−5=1116 – 5 = 1116−5=11
- 3×11=333 \times 11 = 333×11=33
- 2+33=352 + 33 = 352+33=35
Order of operations is fundamental to avoid miscalculations and confusion in both basic and advanced math.
What is the Definition of Period in Math?
In math, a period is the distance or interval required for a repeating pattern or function to complete one full cycle. This concept is often applied to trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent.
Example
The function y=sin(x)y = \sin(x)y=sin(x) has a period of 2π2\pi2π, meaning it repeats its values every 2π2\pi2π units along the x-axis. Understanding the period of a function helps in graphing, predicting behaviour, and solving real-world problems involving cyclical events.
What is the Definition of Slope in Math?
In mathematics, the slope of a line indicates how steep it is and the direction it tilts. It is calculated as the ratio of the vertical difference (rise) to the horizontal difference (run) between any two points on the line.
Formula
slope(m)=riserun=y2−y1x2−x1\text{slope} (m) = \frac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}} = \frac{y_2 – y_1}{x_2 – x_1}slope(m)=runrise=x2−x1y2−y1
Example
For points (2, 3) and (5, 11) on a line
m=11−35−2=83m = \frac{11 – 3}{5 – 2} = \frac{8}{3}m=5−211−3=38
A positive slope indicates a line going upwards, a negative slope a line going downwards, and a zero slope a horizontal line. Slope is fundamental in geometry, physics, and economics.
What is the Math Definition of Distributive Property
The distributive property is a fundamental algebraic rule that allows multiplication to be distributed over addition or subtraction inside parentheses. It ensures expressions are simplified correctly.
Rule
- a(b+c)=ab+aca(b + c) = ab + aca(b+c)=ab+ac
Example
- 3(4+5)=3×4+3×5=12+15=273(4 + 5) = 3 \times 4 + 3 \times 5 = 12 + 15 = 273(4+5)=3×4+3×5=12+15=27
The distributive property is essential in simplifying algebraic expressions, solving equations, and performing mental math efficiently.
What is a Factor in Math
A factor is a number or expression that divides another number or expression exactly, without leaving a remainder. Factors are the building blocks of multiplication.
Example
- The numbers that divide 12 evenly without leaving a remainder are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12; these are called the factors of 12.
- In algebra, xxx is a factor of x2+3xx^2 + 3xx2+3x because x(x+3)=x2+3xx(x + 3) = x^2 + 3xx(x+3)=x2+3x.
Understanding factors is crucial for simplifying expressions, finding greatest common factors, and solving equations.
What is an Exponent in Math
An exponent indicates how many times a base number is used as a factor in repeated multiplication. It provides a concise way to represent repeated multiplication.
Notation
- ana^nan
Here, aaa is the base and nnn is the exponent.
Example
- 24=2×2×2×2=162^4 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 1624=2×2×2×2=16
Exponents are widely used in algebra, calculus, and scientific notation to simplify very large or very small numbers.
How Factors and Exponents Work Together
Understanding factors and exponents is key to mastering many algebraic operations. For instance, the prime factorization of a number uses both concepts:
- 36=22×3236 = 2^2 \times 3^236=22×32
Here, the factors 2 and 3 are expressed using exponents. This combination is crucial in simplifying fractions, solving equations, and studying number theory.
Conclusion
Mathematics may appear complex, but understanding its basic definitions makes it far more approachable. Key terms such as inequality, order of operations, period, slope, distributive property, factor, and exponent form the foundation of algebra, geometry, and advanced mathematical reasoning. By mastering these concepts, students and professionals alike can solve problems with accuracy and confidence.
Whether you are calculating a slope, applying the distributive property, or evaluating exponents, these foundational definitions provide clarity and precision for all levels of mathematics. Remember, every advanced concept in math builds upon these simple, yet powerful, principles.
Learning Tips
- Inequality To understand what is the definition of inequality in math, use number lines and compare real-world values like prices or measurements.
- Order of Operations Remember PEMDAS for what is the definition of order of operations in math. Solve step-by-step to avoid mistakes.
- Period Learn what is the definition of period in math by identifying repeating decimals or cycles in functions.
- Slope For what is the definition of slope in math, practise calculating rise over run on graphs and relate it to slopes in real life.
- Distributive Property Understand the math definition of distributive property by breaking expressions like a(b+c)=ab+aca(b + c) = ab + aca(b+c)=ab+ac and using visual models.
- Factors & Exponents For what is a factor in math definition and what is exponent in math definition, practise listing factors and using repeated multiplication for exponents.
- Practice & Apply Solve problems, draw diagrams, and teach concepts to reinforce understanding of all these key terms.
FAQs
What is inequality in math?
An inequality shows that two values are not equal and may be greater than, less than, or equal in part.
What does slope mean in math?
Slope measures the steepness of a line as the ratio of vertical change to horizontal change.
What is a factor in math?
A factor is a number or expression that divides another exactly without a remainder.
How do exponents work?
Exponents indicate repeated multiplication of a base number by itself.
What is the distributive property?
It allows multiplication to be distributed across addition or subtraction inside parentheses.