Definition of Ordered Pair in Math SAS Unit Rate Congruence and Product
Mathematics forms the foundation of logic, problem-solving, and analytical thinking. Understanding core concepts and definitions is crucial for students, educators, and professionals alike. In this article, we will explore some fundamental math definitions, including what is the definition of math, what is the definition of ordered pair in math, side-angle-side (SAS) in math, unit rate, congruence, and product. We will also provide clear explanations, examples, and practical applications for each concept.
What is the Definition of Math?
Mathematics, commonly known as math, is the study of numbers, shapes, quantities, structures, and patterns. At its core, math provides a systematic way to understand, analyze, and model real-world phenomena. It encompasses various branches such as arithmetic, algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics.
Key Points About Math
- Abstract and Logical Math relies on abstract reasoning and logical steps to solve problems.
- Universal Language Mathematical principles are consistent worldwide, making math a universal language.
- Problem-Solving It provides tools to solve complex problems in science, engineering, economics, and daily life.
Example
Calculating the total cost of items purchased, finding distances on a map, or predicting population growth all require the application of mathematical concepts.
Thus, when someone asks what is the definition of math?, it can be defined as:
- The study of numbers, patterns, quantities, and structures using logical reasoning to solve problems and explain relationships.
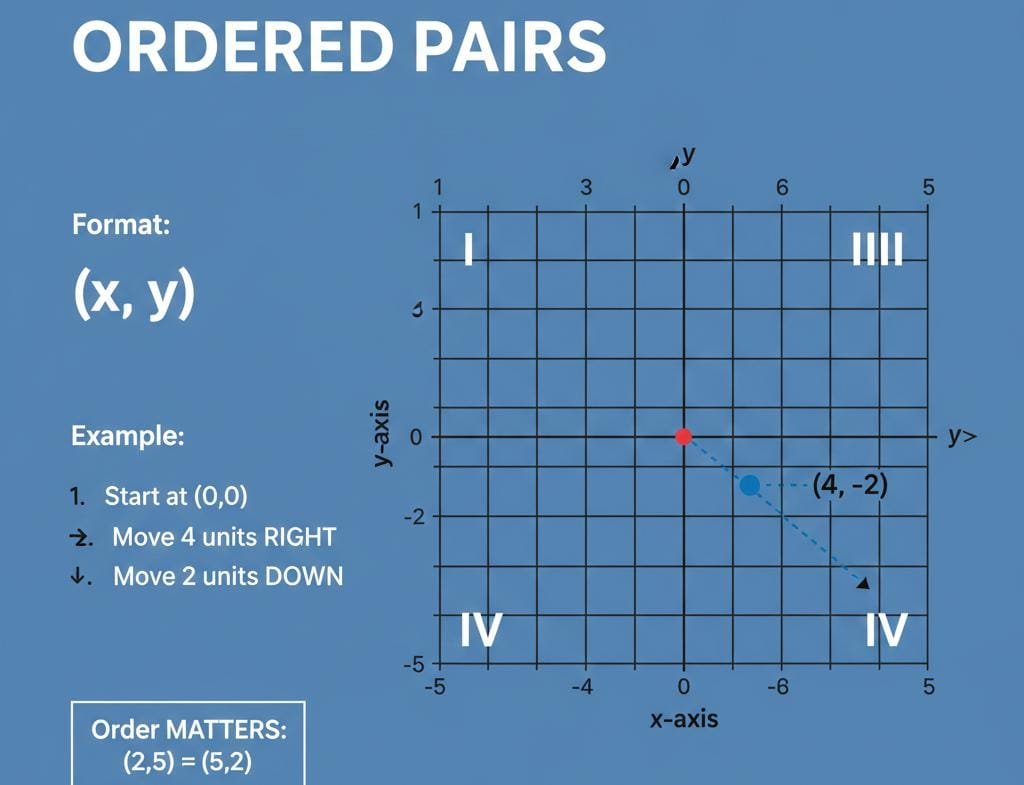
What is the Definition of Ordered Pair in Math?
An ordered pair is a pair of numbers or elements written in a specific order, usually in parentheses as (x,y)(x, y)(x,y). Ordered pairs are used primarily in coordinate geometry to represent points on a Cartesian plane and in set theory to define relations.
Key Features of Ordered Pairs
- The first element is called the x-coordinate (abscissa).
- The second element is called the y-coordinate (ordinate).
- The order is significant: (x,y)≠(y,x)(x, y) \neq (y, x)(x,y)=(y,x) unless x=yx = yx=y.
Example
- (2,5)(2, 5)(2,5) represents a point 2 units right and 5 units up from the origin.
- In set theory, if A={1,2}A = \{1, 2\}A={1,2} and B={a,b}B = \{a, b\}B={a,b}, the Cartesian product A×B={(1,a),(1,b),(2,a),(2,b)}A \times B = \{(1, a), (1, b), (2, a), (2, b)\}A×B={(1,a),(1,b),(2,a),(2,b)}.
Graphing Ordered Pairs
- Start at the origin (0,0)(0, 0)(0,0).
- Move horizontally to the x-coordinate value.
- Move vertically to the y-coordinate value.
- Mark the point where you stop.
Using ordered pairs, students can plot points, identify quadrants, and calculate distances between points.
What is the Definition of Side-Angle-Side (SAS) in Math
Side-Angle-Side (SAS) is a geometric postulate used to determine triangle congruence. It states that if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
Key Features of SAS
- Involves two sides and the angle between them.
- Ensures that triangles are identical in shape and size.
- Does not apply if the angle is not between the two sides.
Example
If triangle ABC has sides AB = 5 cm, AC = 7 cm, and ∠A = 60°, and triangle XYZ has sides XY = 5 cm, XZ = 7 cm, and ∠X = 60°, then ΔABC ≅ ΔXYZ by SAS.
SAS is widely used in geometry for constructing congruent triangles, proving properties of shapes, and solving geometric problems.
What is the Definition of Unit Rate in Math?
A unit rate compares two quantities, expressing one quantity as a single unit. People commonly use unit rates to calculate speed, cost per item, or efficiency.
Key Features of Unit Rate
- Expressed as per one (e.g., miles per hour, price per kilogram).
- Helps simplify comparisons between different quantities.
Example
- A car travels 150 miles in 3 hours. Unit rate = 150 ÷ 3 = 50 miles per hour.
- If 5 kg of apples cost $20, the unit rate = 20 ÷ 5 = $4 per kg.
Unit rates are practical for everyday life and in solving math word problems related to ratios, percentages, and proportions.
What is the Math Definition of Congruence (Simple)
Congruence in math refers to the condition where two figures have the same shape and size. Congruent shapes can be moved, rotated, or flipped without altering their dimensions.
Key Features of Congruence
- Two triangles, for example, are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are equal.
- Congruence can be tested using postulates like SAS, SSS (Side-Side-Side), and ASA (Angle-Side-Angle).
Example
- Triangle ABC with sides 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm is congruent to triangle XYZ with sides 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm.
- Denoted as: ΔABC ≅ ΔXYZ
Understanding congruence is crucial for geometry, symmetry analysis, and construction problems.
What is the Math Definition of Product?
In mathematics, a product is the outcome obtained when two or more numbers are multiplied. This concept is essential in both arithmetic and algebra.
Key Points About Product
- Represented as a×ba \times ba×b or simply ababab.
- Can involve whole numbers, fractions, decimals, or variables.
- Used in various applications including area calculation, scaling, and problem-solving.
Examples
- 5×3=155 \times 3 = 155×3=15
- 23×34=612=12\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{3}{4} = \frac{6}{12} = \frac{1}{2}32×43=126=21
- x×y=xyx \times y = xyx×y=xy
Products form the basis for more complex operations like exponents, matrix multiplication, and polynomial multiplication.
How These Definitions Work Together
Mathematics is interconnected, and understanding these definitions can help solve complex problems:
- Math is the overarching discipline.
- Ordered pairs allow precise plotting of points and functions.
- SAS and congruence ensure geometric figures are correctly compared and constructed.
- Unit rate enables practical comparisons in real life.
- Product provides the basis for calculations, formulas, and problem-solving.
Example
To solve a geometry problem, you might calculate distances using products, plot points using ordered pairs, and prove triangles congruent using SAS.
Practical Examples
Example 1
Plotting a point using an ordered pair
- Point: (4, -3)
- Move 4 units right, 3 units down Quadrant IV
Example 2
Using SAS to prove congruence
- Triangle ABC with sides AB = 6, AC = 8, and ∠A = 90°
- Triangle XYZ with sides XY = 6, XZ = 8, and ∠X = 90°
- Triangles are congruent (ΔABC ≅ ΔXYZ)
Example 3
Calculating a unit rate
- 300 km in 5 hours 300 ÷ 5 = 60 km/h
Example 4
Calculating product
- 12 × 15 = 180
Conclusion
Understanding the definition of math and related concepts like ordered pairs, SAS, unit rate, congruence, and product is essential for mastering mathematics. These concepts are interconnected and form the foundation for problem-solving, geometry, algebra, and real-world applications. By practicing these concepts with examples and exercises, students can build confidence and improve their mathematical skills.
Mastering these definitions will allow learners to graph points, solve ratios, prove congruence, and perform accurate calculations, laying the groundwork for advanced math topics.
Quick Learning Tips
- Understand Math Basics Know what is the definition of math; visualise numbers, shapes, and patterns.
- Plot Ordered Pairs Learn what is the definition of ordered pair in math; use graphs to see points (x, y).
- Use SAS in Triangles Understand side-angle-side in math; draw triangles to visualise congruence.
- Apply Unit Rate Solve real-life problems with unit rate in math like speed or cost per item.
- Simplify Congruence Math definition of congruence simple: identical in shape and size; use cut-outs.
- Practice Products Math definition of product: result of multiplication; practice with numbers or algebra.
FAQs
Why is the order important in an ordered pair?
Because it determines the exact position on a coordinate plane. (x,y)≠(y,x)(x, y) \neq (y, x)(x,y)=(y,x).
How does SAS help in geometry?
SAS confirms triangle congruence by comparing two sides and the included angle.
What are common real-life examples of unit rates?
Speed (km/h), cost per item, fuel efficiency (miles per gallon).
How is the product different from sum?
The product is multiplication, while the sum is addition.
What does congruence indicate in geometry?
Congruence ensures shapes have the same size and shape.