Definition of Mean Math Median Mode and Trigonometry Formulas
Mathematics is not just a subject it is a way to interpret the world using numbers, patterns, and relationships. Among its foundational concepts are mean, median, mode, and trigonometry, which are essential for data analysis, problem-solving, and understanding geometry. These concepts are widely applied in academics, real-life scenarios, and even professional fields like engineering, finance, and data science. In this article, we will explore what is the definition of mean math, what is the definition of median in math, what is the definition of mode in math, and what is the definition of trigonometry in math, along with practical examples and applications.
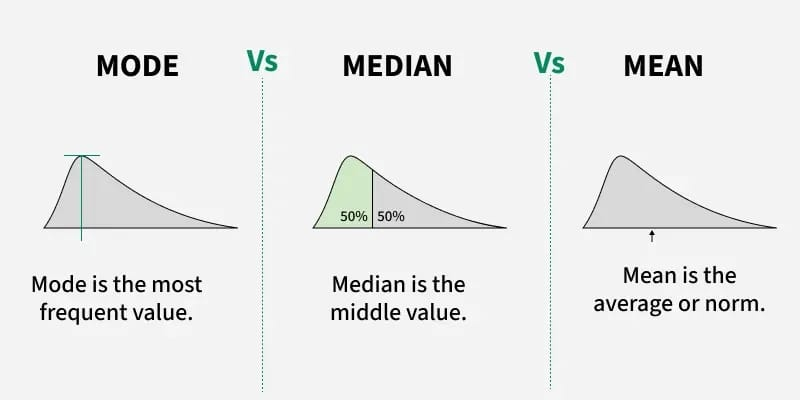
What is the Definition of Mean Math?
The mean is one of the most common measures of central tendency in mathematics. It is also referred to as the arithmetic average. Essentially, the mean provides a single value that represents the central point of a set of numbers. Understanding the mean helps summarize large data sets efficiently.
How to Calculate the Mean
The formula for the mean is simple
Mean=Sum of all numbersTotal number of numbers\text{Mean} = \frac{\text{Sum of all numbers}}{\text{Total number of numbers}}Mean=Total number of numbersSum of all numbers
Example
Consider the data set 4, 8, 6, 5, 3.
- Sum the numbers 4 + 8 + 6 + 5 + 3 = 26
- Count the total numbers 5
- Divide the sum by the total number 26 ÷ 5 = 5.2
So, the mean of this data set is 5.2.
The mean is particularly useful when dealing with evenly distributed data. However, it can be affected by extremely high or low values, known as outliers.
Applications of Mean
- Education Calculating students average grades.
- Economics Finding the average income of a population.
- Finance Estimating the average return on investment.
- Science Summarizing experimental data for analysis.
By understanding what is the definition of mean math, students and professionals can quickly interpret numerical information, making it a cornerstone of statistical analysis.
What is the Definition of Median in Math?
The median is another important measure of central tendency. Unlike the mean, the median represents the middle value of a data set when the numbers are arranged in ascending or descending order. This makes the median less affected by outliers, providing a more accurate central value for skewed data.
How to Calculate the Median
- Arrange the numbers in order from smallest to largest.
- If the total number of values is odd, the median is the middle number.
- For data sets with an even quantity of values, the median lies halfway between the two middle numbers.
Example 1 (Odd Number of Values)
- Data set: 3, 7, 9, 5, 11
- Arrange in order: 3, 5, 7, 9, 11
- Median = 7 (middle number)
Example 2 (Even Number of Values)
- Data set: 4, 8, 6, 2
- Arrange in order: 2, 4, 6,
- Median = (4 + 6) ÷ 2 = 5
Applications of Median
- Housing Market Determining the median house price to avoid extreme values.
- Income Analysis Calculating median income gives a better sense of typical earnings than the mean when high earners exist.
- Healthcare Median recovery time for treatments can provide more accurate insights.
Understanding what is the definition of median in math is crucial for interpreting data that may be skewed or contain outliers.
What is the Definition of Mode in Math?
The mode is the number or value that occurs most frequently in a data set. Unlike the mean and median, a data set may have no mode, one mode (unimodal), or multiple modes (bimodal or multimodal). The mode is particularly useful in identifying the most common occurrence within a data set.
How to Calculate the Mode
- Count how many times each number appears.
- Identify the number(s) with the highest frequency.
Example
Data set: 2, 3, 4, 2, 5, 2, 3
- Frequency of 2 = 3 times
- Frequency of 3 = 2 times
- Frequency of 4 = 1 time
- Frequency of 5 = 1 time
Mode = 2 (most frequent number)
Applications of Mode
- Retail Determining the most sold product.
- Survey Analysis Finding the most common answer.
- Healthcare Most common symptom reported in a study.
By knowing what is the definition of mode in math, analysts can identify trends and patterns in categorical and numerical data sets.
Understanding Trigonometry in Math
Trigonometry is a mathematical discipline concerned with analysing the relationships between triangle angles and their corresponding sides. Derived from Greek words meaning triangle and measurement, trigonometry is fundamental to geometry, physics, engineering, astronomy, and computer graphics.
Basic Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometry is based on three primary ratios for right-angled triangles:
- A trigonometric function that represents the proportion between the opposite side and the hypotenuse.
sinθ=oppositehypotenuse\sin \theta = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}}sinθ=hypotenuseopposite
- A trigonometric function that expresses the relationship between the adjacent side and the hypotenuse of an angle.
cosθ=adjacenthypotenuse\cos \theta = \frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}}cosθ=hypotenuseadjacent
- Tangent (tan): A trigonometric ratio that measures the relationship between the opposite side and the adjacent side of an angle.
tanθ=oppositeadjacent\tan \theta = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}}tanθ=adjacentopposite
These ratios are fundamental for solving problems involving angles and distances.
Applications of Trigonometry
- Engineering Calculating forces, angles, and distances in structures.
- Navigation Using angles to determine locations in aviation and marine navigation.
- Astronomy Measuring distances to stars and planets.
- Computer Graphics Rendering 3D objects using trigonometric functions.
Understanding what is the definition of trigonometry in math allows students and professionals to apply these concepts to solve practical problems in both academic and real-world contexts.
Relationship Between Mean, Median, and Mode
The mean, median, and mode are all measures of central tendency, and they often provide complementary insights:
- Mean Provides a precise average but is sensitive to extreme values.
- Median Gives a middle value, reducing the effect of outliers.
- Mode Highlights the most frequently occurring value.
Empirical Relationship (For Skewed Data)
For certain data sets, an empirical relationship can estimate one measure from others:
Mode≈3×Median−2×Mean\text{Mode} \approx 3 \times \text{Median} – 2 \times \text{Mean}Mode≈3×Median−2×Mean
This formula is particularly useful when dealing with large data sets in statistics and business analytics.
Practical Examples Combining Mean, Median, Mode, and Trigonometry
Let’s see a combined application
Scenario A civil engineer is designing a triangular bridge support and needs to analyse survey data for weight loads.
- Data Set of Weights (in tons): 5, 8, 5, 12, 7, 5, 10
- Mean weight = (5+8+5+12+7+5+10)/7 = 7.43 tons
- Median weight = 7 tons (middle value)
- Mode weight = 5 tons (most frequent)
- Trigonometry: The engineer calculates angles and lengths of the triangular supports using sine, cosine, and tangent to ensure structural stability.
This example shows how statistical measures and trigonometry together inform practical decision-making.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mean Calculation Errors: Forgetting to sum all numbers or miscounting the total number of values.
- Median Confusion Not arranging numbers in order before identifying the middle value.
- Mode Misinterpretation Overlooking multiple modes or assuming a mode exists when all numbers are unique.
- Trigonometry Misuse Confusing opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse sides in triangle calculations.
Conclusion
Understanding what is the definition of mean math, what is the definition of median in math, what is the definition of mode in math, and what is the definition of trigonometry in math is essential for students, professionals, and anyone who deals with numbers or geometry. These concepts provide a foundation for statistical analysis, data interpretation, and practical problem-solving in everyday life and advanced fields like engineering, finance, and computer science.
Whether you are a student preparing for exams or a professional working with data, these mathematical tools are indispensable. Consistent practice, worksheets, and problem-solving exercises can strengthen your understanding and ability to apply these concepts effectively.
Learning Tips
- Understand what is the definition of mean math before solving averages.
- Arrange numbers first to find the definition of median in math correctly.
- Look for repeated values when applying the definition of mode in math.
- Use diagrams to better grasp the definition of trigonometry in math.
FAQs
What is the definition of mean math?
The mean is the average of a data set, found by dividing the total of all values by how many values there are.
What is the definition of median in math?
The median is the middle value when numbers are arranged in order. If there are two middle values, their average is the median.
What is the definition of mode in math?
The mode is the value that occurs most often in a data set.
What is the definition of trigonometry in math?
Trigonometry is a branch of math that studies relationships between angles and sides of triangles.