Definition of Base in Math Unit Rate Equation Factor Integer & Variable
Mathematics is more than just numbers and operations; it is a language of logic and problem solving. Every mathematical concept builds upon fundamental definitions that students must understand clearly to succeed. Understanding concepts like base, math expressions, unit rate, equations, factors, integers, multiples, product, and variables is crucial for mastering algebra, geometry, and arithmetic.
In this article, we will provide detailed explanations, practical examples, and tips for learning these essential math concepts. Each keyword will be discussed thoroughly to help students, educators, and math enthusiasts understand and apply these terms effectively.
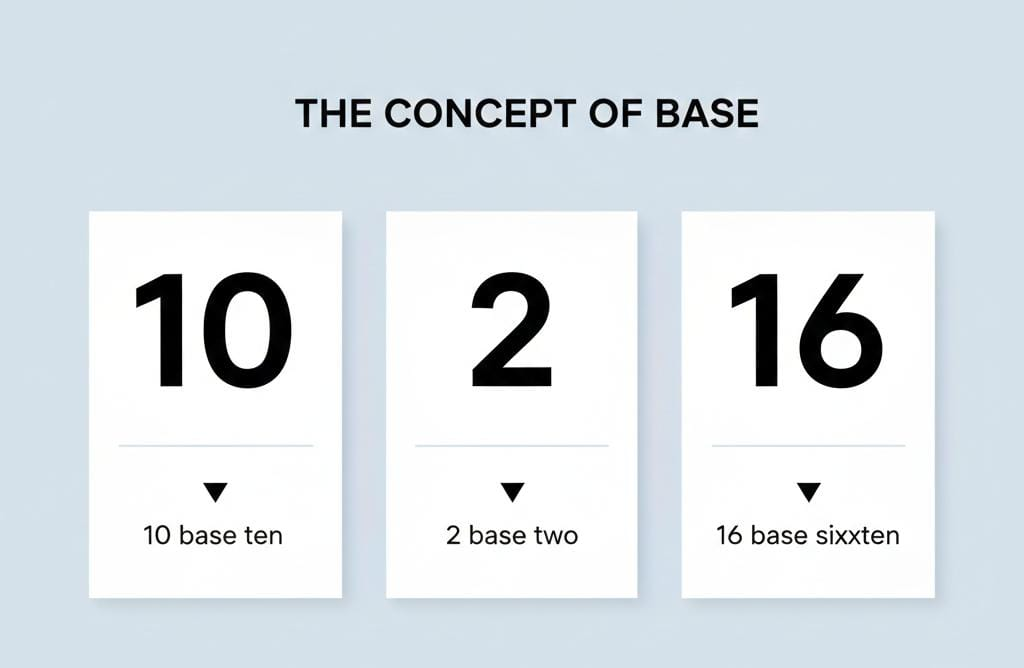
What Is the Definition of Base in Math
In mathematics, the base (also called radix) refers to the number of distinct digits or symbols used in a number system to represent numbers. The concept of base is foundational to understanding number systems such as binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal.
Number Systems and Bases
- Binary (Base-2) Uses digits 0 and 1. Computers operate using this system.
- Decimal (Base-10) Uses digits 0–9 and is the most widely used system in daily life.
- Octal (Base-8) Uses digits 0–7. Often used in computer programming.
- Hexadecimal (Base-16) Uses digits 0–9 and letters A–F. It is commonly used in computing and digital electronics.
Example
The decimal number 25 in binary (base-2) is represented as 11001₂.
Importance of Base in Math
The base determines the place value of each digit in a number. For instance, in base-10, the number 345 means 3 hundreds, 4 tens, and 5 units. Understanding bases allows students to convert numbers between systems, which is critical in programming, computer science, and advanced mathematics.
What Is the Definition of a Math Expression
A mathematical expression is a combination of numbers, variables, and mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. Expressions are fundamental in algebra because they represent quantities and relationships without asserting equality.
Components of a Math Expression
- Constants Fixed numbers in the expression, e.g., 5 in 3x + 5.
- Variables Symbols that represent unknown values, usually letters like x, y, or z.
- Coefficients Numbers multiplying variables, e.g., 3 in 3x.
- Terms Single parts of an expression, either a constant, a variable, or a product of both.
Types of Mathematical Expressions
- Arithmetic Expressions Contain only numbers and operations, e.g., 7 + 4 × 2.
- Algebraic Expressions Contain variables and constants, e.g., 3x² − 2x + 5.
- Fractional Expressions Contain ratios of expressions, e.g., (2x + 3)/(x − 5).
Difference Between Expression and Equation
- Expression: Represents a value, e.g., 2x + 5.
- Equation: Represents equality, e.g., 2x + 5 = 15.
Simplifying and manipulating expressions is essential for solving equations and understanding advanced algebraic concepts.
What Is the Definition of Unit Rate in Math
A unit rate is a type of ratio that compares a quantity to one unit of another quantity. Unit rates are extremely useful in everyday life, such as calculating speed, cost per item, or conversion of units.
Example of Unit Rate
- 35 miles in 1 hour 35 miles per hour (mph).
- 20 dollars for 5 books 4 dollars per book.
How to Find Unit Rate
- Identify the total quantities in the ratio.
- Divide both numbers by the quantity on the right side to reduce it to per 1 unit.
Unit rates help students understand ratios and proportions and make comparisons more straightforward. They are particularly useful in real-world applications such as shopping, travel, and physics.
What Is the Definition of an Equation in Math
An equation is a mathematical statement showing that two expressions have the same value. Unlike expressions, equations include an equal sign (=) and can be solved to determine unknown numbers.
Example of an Equation:
- 2x + 3 = 11 Solving gives x = 4.
- 4y − 5 = 15 Solving gives y = 5.
Equations are central in algebra because they allow us to model real-world problems mathematically, find unknown quantities, and verify relationships between numbers.
What Is the Definition of Factor in Math?
A factor is a number or expression that divides another number or expression completely without leaving a remainder. Understanding factors is crucial for simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations.
Examples
- Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12.
- Factors of x² + 5x + 6 are (x + 2)(x + 3).
Factors also play a significant role in calculating multiples, greatest common divisors (GCD), and least common multiples (LCM), which are essential for arithmetic operations and algebra.
What Is the Definition of an Integer in Math
An integer is a whole number that can be positive, negative, or zero. Integers do not include fractions, decimals, or non-whole numbers.
Examples of Integers
- −5, 0, 7, 14
- Non-integers: 3.5, 0.25
Integers are used extensively in counting, solving equations, and number theory. They form the basis of operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division in advanced mathematics.
What Is the Definition of a Multiple in Math
A multiple is a number obtained by multiplying a given number by an integer. Multiples are closely related to factors and are essential for understanding patterns in numbers.
Example
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20…
- Multiples of x: 2x, 3x, 4x…
Multiples are used in calculating LCM, solving divisibility problems, and understanding sequences and patterns.
What Is the Definition of Product in Math Terms?
The product is the result obtained when two or more numbers or expressions are multiplied together.
Example:
- 4 × 5 = 20 20 is the product.
- (x + 3)(x − 2) = x² + x − 6 The expanded result is the product.
Products are vital in arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and applied mathematics. Understanding products helps in factoring expressions, solving equations, and calculating areas and volumes in geometry.
What Is the Definition of a Variable in Math?
A variable is a symbol, often a letter, used to represent an unknown or changeable value. Variables are foundational in algebra and are essential for representing relationships, functions, and equations.
Examples
- In y = 3x + 5, x and y are variables.
- Variables can take different values depending on the context of the problem.
Importance of Variables
Variables allow mathematicians to generalize patterns, create formulas, and solve complex real-world problems using equations and expressions.
Practice Problems
- Convert decimal 18 to binary.
Answer: 10010₂ - Simplify 5x + 3x − 7 + 2.
Answer: 8x − 5 - Find the unit rate for 50 miles in 2 hours.
Answer: 25 mph - Solve the equation 3x − 4 = 11.
Answer: x = 5 - List the factors of 24.
Answer: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 - Identify multiples of 7 under 50.
Answer: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49 - Find the product of x + 2 and x − 3.
Answer: x² − x − 6 - Identify the variables in 2y² + 3y − 5.
Answer: y
Key Points
- Base in Math Determines the number of digits in a number system; practice conversions between binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal.
- Math Expression Made up of constants, variables, and terms; simplify using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Unit Rate in Math A ratio per 1 unit; use for speed, cost, or distance problems.
- Equation in Math A statement with an equal sign; isolate variables and check solutions.
- Factor in Math Numbers or expressions that divide exactly; use to simplify or find multiples.
- Integer in Math Whole numbers including negatives, positives, and zero; practice operations on a number line.
- Multiple in Math Products of a number with integers; use multiplication tables for practice.
- Product in Math Terms: Result of multiplication; applies to numbers, expressions, area, and volume.
- Variable in Math Unknown or changeable values; practice substituting and solving equations.
Conclusion
Mastering these fundamental mathematical terms base, math expressions, unit rate, equations, factors, integers, multiples, product, and variables is critical for students aiming to excel in mathematics. These concepts form the backbone of algebra, arithmetic, geometry, and real-life problem-solving.
By practicing examples, solving equations, understanding number systems, and working with expressions, students build confidence and competence in math. Always remember: clear understanding of base, variables, factors, and products helps in simplifying complex problems, calculating ratios and unit rates, and exploring advanced mathematics.
FAQs
What is the base in math?
The base refers to the number of digits used in a number system, also called radix.
What is the difference between an expression and an equation?
Expressions represent a value without an equal sign, while equations assert equality between two expressions.
How do you calculate a unit rate?
Divide the quantity on the left by the quantity on the right to compare “per one unit.”
What are integers?
Integers are whole numbers that include positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero.
What is a factor?
A factor divides another number or expression completely without a remainder.
What is the product in math?
The product is the result of multiplying two or more numbers or expressions.