Definition of Divisor in Math Probability Isometry Triangles & More
Mathematics is a subject built on clear definitions and logical relationships. Whether you are a school student, teacher, or self-learner, understanding precise mathematical terminology is essential for problem-solving and conceptual clarity. Concepts such as divisors, empirical probability, isometry, midpoint theorem, and probability distributions form the backbone of arithmetic, geometry, and statistics.
This comprehensive guide explains the definitions of essential maths terms in a clear, structured, and easy-to-understand way. Each concept is explored with examples and explanations to support deep understanding and academic success.
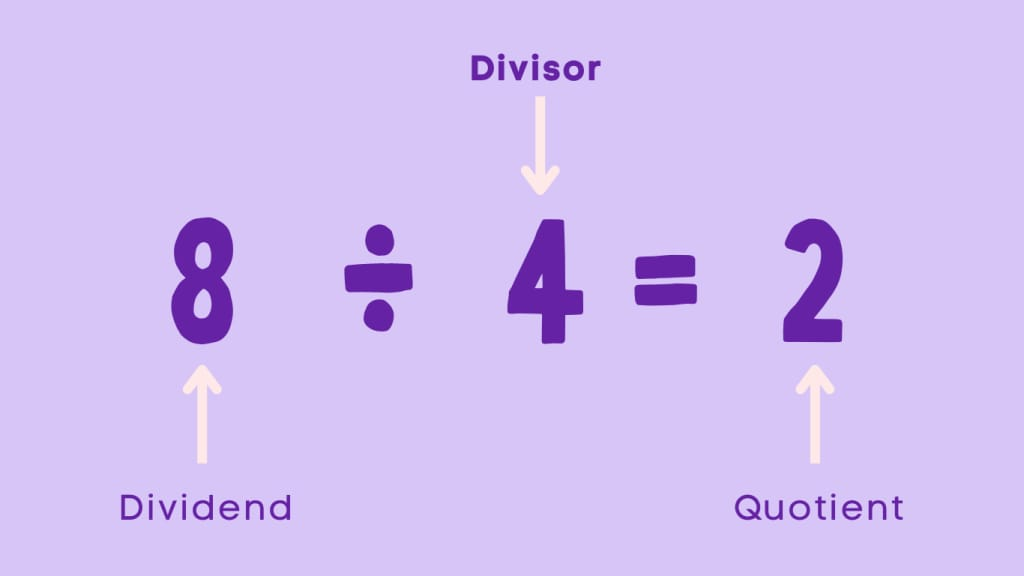
What Is the Definition of Divisor in Math?
In mathematics a divisor is a number that divides another number, known as the dividend, to produce a whole number result.
Formal Definition
A divisor is an integer that divides a given number exactly, leaving no remainder.
Example
- 24 ÷ 6 = 4 → 6 is a divisor of 24
- 24 ÷ 5 = 4.8 → 5 is not a divisor of 24
Divisors are closely related to factors and play a crucial role in identifying prime and composite numbers. Every whole number has at least two divisors: 1 and itself.
What Does Empirical Probability Mean in Mathematics?
Empirical probability is a type of probability based on observed data from experiments, rather than theoretical expectations.
Definition
Empirical probability represents the proportion of times an event occurs compared to the total trials conducted.
Formula
Empirical Probability=Number of successful outcomesTotal number of trials\text{Empirical Probability} = \frac{\text{Number of successful outcomes}}{\text{Total number of trials}}Empirical Probability=Total number of trialsNumber of successful outcomes
Example
- If a coin lands on heads 45 times out of 100 tosses:
- 45100=0.45\frac{45}{100} = 0.4510045=0.45
- Empirical probability is widely used in statistics, experiments, and real-world data analysis.
What Is the Definition of Isometry in Math?
An isometry is a geometric transformation that preserves distance, size, and shape.
Definition
An isometry is a transformation that preserves the shape and size of a figure, making the original and its image congruent.
Types of Isometries
- Translation
- Rotation
- Reflection
After an isometry, the figure may change position or orientation, but its measurements remain unchanged. Isometries are fundamental in geometry and transformational mathematics.
What Is the Definition of the Midpoint Theorem in Math?
The midpoint theorem applies specifically to triangles and describes the relationship between midpoints and parallel sides.
Definition
The line linking the midpoints of two triangle sides is parallel to the remaining side and exactly half as long.
Importance
- Used in geometric proofs
- Helps find unknown lengths
- Supports understanding of similarity and parallel lines
This theorem is essential in coordinate geometry and triangle properties.
What Is the Definition of Midsegment in Math?
A midsegment is closely related to the midpoint theorem.
Definition
A midsegment is a line segment that joins the midpoints of two sides of a polygon, most commonly a triangle.
Key Properties
- It is parallel to the third side
- Its length is half the length of the third side
Midsegments are useful in solving length and similarity problems in geometry.
What Is the Definition of Range in Math?
The range measures how spread out a set of data is.
Definition
In statistics, the range is the difference between the maximum and minimum values in a set of data.
Formula
Range=Maximum value−Minimum value\text{Range} = \text{Maximum value} – \text{Minimum value}Range=Maximum value−Minimum value
Example:
- For the data set {3, 7, 10, 15}
- 15−3=1215 – 3 = 1215−3=12
- Range is a basic yet important concept in statistics and data handling.
What Is the Definition of Remainder in Math?
A remainder is what is left after dividing one number by another when the division is not exact.
Definition
The remainder is the amount left over when a dividend is divided by a divisor.
Example
- 17 ÷ 5 = 3 remainder 2
Remainders are essential in division, modular arithmetic, and real-world applications such as grouping and sharing.
What Is the Definition of Side-Side-Side (SSS) in Math?
Side-Side-Side (SSS) is a triangle congruence rule.
Definition
If the three sides of a triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, the triangles are considered congruent.
Why It Matters
- Proves triangles are exactly the same size and shape
- Used in geometry proofs
- Ensures angle equality indirectly
SSS is one of the most reliable methods for proving triangle congruence.
What Is the Definition of Similar Triangles in Math
Similar triangles have the same shape but may differ in size.
Definition
Two triangles are similar if:
- Their corresponding angles are equal
- Their corresponding sides are in the same ratio
Example
If one triangle has sides 3, 4, 5 and another has sides 6, 8, 10, they are similar.
Similar triangles are used extensively in trigonometry, measurement, and real-life scaling problems.
What Is the Math Definition of Combination?
In mathematics, a combination refers to selecting objects where order does not matter.
Definition
A combination is a selection of items from a larger group without regard to order.
Formula
nCr=n!r!(n−r)!nCr = \frac{n!}{r!(n-r)!}nCr=r!(n−r)!n!
Example
Choosing 2 students from a group of 5 is a combination, not a permutation.
Combinations are fundamental in probability and statistics.
What Is the Math Definition of Probability Distribution?
A probability distribution provides a summary of the probabilities for every possible outcome of a random variable.
Definition
A probability distribution is a function or table that shows the probability of each possible outcome of an experiment.
Key Rules
- Probabilities lie between 0 and 1
- Total probability equals 1
Types
- Discrete probability distribution
- Continuous probability distribution
Probability distributions are crucial in statistics, data science, and real-world predictions.
What Is the Math Definition of Similarity
Simple Definition
Similarity in maths means figures have the same shape but may have different sizes.
Key Characteristics
- Corresponding angles are equal
- Corresponding sides are proportional
Similarity is commonly used in geometry, maps, models, and scale drawings.
Why These Mathematical Definitions Matter
Understanding precise mathematical definitions:
- Improves problem-solving skills
- Builds a strong foundation for advanced maths
- Helps students succeed in exams
- Encourages logical and analytical thinking
Each concept explained above connects directly to core curriculum topics across arithmetic, geometry, and statistics.
Conclusion
Mathematics relies on accuracy, clarity, and structured understanding. By mastering definitions such as divisor, empirical probability, isometry, midpoint theorem, probability distribution, and similarity, learners develop confidence and competence in mathematics. This guide provides a complete, student-friendly explanation of essential mathematical terms, making it a valuable reference for learning, revision, and exam preparation.
Each concept is explained with clear examples and practical applications, helping students see how abstract ideas connect to real-world problems. Whether you are a beginner or preparing for advanced exams, this guide ensures a solid foundation in core mathematical principles.
Learning Tips
- Understand the Concept, Don’t Memorise: Focus on the meaning of terms like divisor, remainder, and range before trying to memorise examples.
- Use Visual Aids Draw triangles for midpoint theorem, midsegment, SSS, and similar triangles to see relationships clearly.
- Practice Probability Conduct experiments to calculate empirical probability and compare it with theoretical probability.
- Solve Step-by-Step When working with combinations or probability distributions, break problems into smaller steps.
- Connect Similar Concepts Link isometry and similarity to transformations to see patterns in geometry.
- Use Real-Life Examples Apply range, remainder, or divisor concepts to practical problems like distributing objects or analysing data.
- Check Your Work Verify triangle problems using SSS or midpoint theorem to ensure accuracy.
- Mix Practice Problems Combine exercises on probability distribution, empirical probability, and combinations to strengthen understanding.
FAQs
What is the definition of divisor in math?
A divisor is a number that divides another number exactly without leaving a remainder. For example, 4 is a divisor of 24 because 24 ÷ 4 = 6.
What is the definition of empirical probability in math?
Empirical probability is calculated based on actual experiments or observations rather than theoretical reasoning. It is the ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total trials.
What is the definition of isometry in math?
An isometry is a transformation that preserves distances and shapes. Examples include rotations, reflections, and translations.
What is the definition of range in math?
In mathematics, the range is the difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set or the set of all possible outputs of a function.
What is the definition of remainder in math?
The remainder is what is left over after division when a number does not divide evenly. For example, in 17 ÷ 5, the remainder is 2.
What is the math definition of combination?
A combination is a way of selecting items from a set where the order does not matter. The formula is C(n,r)=n!r!(n−r)!C(n, r) = \frac{n!}{r!(n-r)!}C(n,r)=r!(n−r)!n!.
What is the math definition of probability distribution?
A probability distribution lists all possible outcomes of a random variable and their probabilities. It can be discrete (e.g., rolling dice) or continuous (e.g., heights).